Basic considerations:
-
The camera, describing VIOSO native coordinate system
- By positioning the test image and entering the radius and start angle, you name a 3D coordinate for every projector pixel on screen.
- This is like a measured point with some tolerance in the real world.
- View poses must use the same eye point.
-
A main view direction and eye point, describing the correspondence between IG and VIOSO
- All views have same eye point.
- There is no fix eye in IG — the eye can be everywhere in the virtual world.
- There is a main view direction. This is where we go “forward”.
- So every view is just an angular offset (yaw, pitch, roll angle) to that main view.
-
Offset angles to a main view
- IG’s forward.
- View from eye “forward” to screen.
- Starting at SPCalibrator 4.3, it became easier, as we can use relative angles now.
To position a camera somewhere else, here is the workflow on how to position a fisheye camera at 2m height on a 4m diameter / 3m height cropped dome (220°x120°) screen.
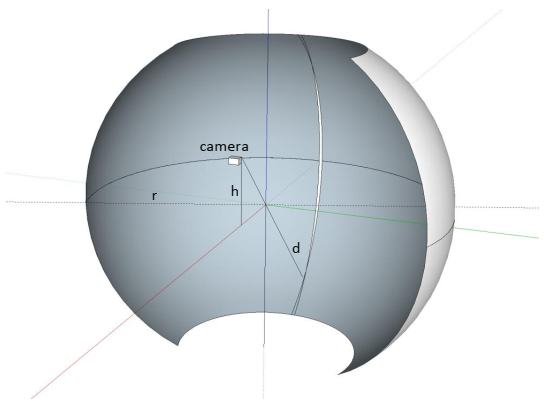
-
Use HQ calibration kit. It comes with a 185° lens and very sensitive sensor
- Fix your camera at 2m height facing the screen.
- The central ray must go through the center of the imaginary sphere that the screen is part of.
- Go as far back as you need to see your whole screen. If the upper left/right corner does not have any projection on it, you may need to move closer.
-
Adjust “Dome master” test image:
- Pole is now where the central ray of the camera hits the screen.
- Image is now pitched down.
- Fill projection. Make longitudes straight.
- Latitudes are circles.
- Do not try to line up outer circle with screen — just cover the screen using 4-point warp.
-
Now figure the angles
-
Find out which pitch the main view has
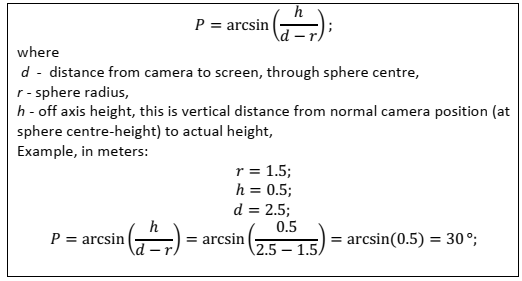
- ZERO (0,0,0) is still the sphere center.
- Figure start angle
- There are 10 latitude lines on our test image, numbered (0,) 10, 20, .. 90 (, 100), like percentages.
- Figure which would be the equator of a globe (you might even think of some extra line somewhere between).
- The number E gives a ratio:

- For example: Equator (biggest circle) is the middle of line 70 and 80. This makes E=75%, thus

- Use this angle in “fisheye to spherical dome”-conversion.
- Figure view poses
- Eye is always 0,0,0.
- View poses are basically the same as with a standard camera position, but pitched.
- Create “main view”, which is pitched (rotation around x) by 30°, -y is up, that makes roll (rotation around z) 180°.
- Do auto pose.
- Use “main view” as relative view (SPCalibrator Version 4.3).
- Make them nice. They should be the same as the ones used in VRSG before. Remember: screen, projector position, and “forward” have not changed!
-
Find out which pitch the main view has